College Coaches Paid with Split-Dollar Life Insurance

This article was originally published to Financial Advisor Magazine.
In August 2016, the University of Michigan began what has now become a trend when they offered a split-dollar life insurance arrangement to head football coach Jim Harbaugh as an alternative to deferred compensation. Other schools have since followed in Michigan’s footsteps: Clemson, for Dabo Swinney; LSU, for Ed Orgeron; and South Carolina, for women’s basketball coach Dawn Staley.
While Michigan’s basketball team finished the 2019-2020 season with a solid but unremarkable record of 19-12 under new head coach Juwan Howard, cooling off (due, in part, to injuries) after an unexpectedly hot 8-1 start that included wins over Gonzaga and North Carolina, Howard has quietly compiled the #4 recruiting class in the country (#1 in the Big Ten). He seems poised to pick up where John Beilein left off and have Michigan contending for national titles on an annual basis for years to come. Like Michigan did with Harbaugh at the completion of his first season as head coach, now is the time for Michigan to enter into a split-dollar life insurance arrangement with Coach Howard.
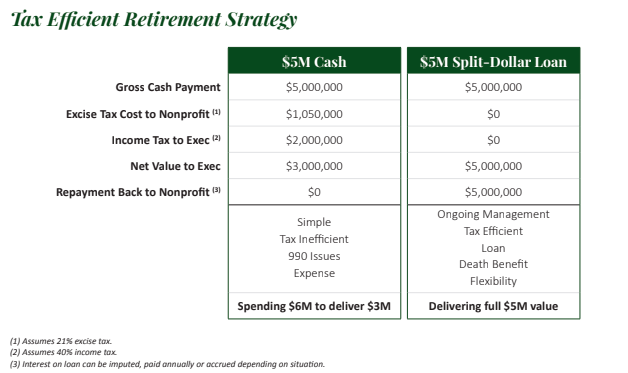
The Benefits Of Split-Dollar Life Insurance
For those unfamiliar with split-dollar life insurance arrangements: This is a program where an employer agrees to loan dollars to an employee (generally over a period of seven years) that are invested in a cash accumulation life insurance policy. Unlike a traditional life insurance policy, however, where the goal is to pay the lowest premium for the highest amount of death benefit, the policies used in these programs do the opposite and pay the highest premium for the lowest amount of death benefit. This approach minimizes policy charges and allows the policy’s cash value to grow as rapidly as possible with the least amount of drag.
At some point—either out of policy cash value during the employee’s lifetime, or out of the death benefit at the employee’s death, depending upon the structure of the agreement—the loan from the employer will be repaid. But in the meantime, policy cash value in excess of the loan balance can be accessed by the employee income tax-free to supplement cash flow in retirement. Think of the arrangement as analogous to the employer funding a Roth IRA for the benefit of the employee, with a potential death benefit as an added bonus.
‘Every Day We Get Better, Or We Get Worse’
As legendary Michigan football coach Bo Schembechler preached, even successful programs always have room for improvement—and Michigan’s approach to split-dollar life insurance is no exception. In designing a new a split-dollar arrangement for Coach Howard, Michigan has the opportunity to upgrade the structure that was used for Coach Harbaugh in ways that would provide significant additional benefit to both the University and the Coach.
“Those Who Stay Will Be Champions.”
One somewhat surprising element of Michigan’s split-dollar agreement with Harbaugh was that it did not include any penalty for leaving early and taking another coaching job somewhere else. While Harbaugh needs to be employed by Michigan at the time of each scheduled advance in order to receive that premium advance, the obligation to repay the earlier premiums is not accelerated in the event of his early departure from the University. Moreover, Harbaugh’s loan is non-interest bearing and non-recourse, so there is little incentive for him to remain with the school once all seven premiums have been advanced. This time around, Michigan should structure Howard’s agreement so that the loan accelerates and becomes immediately due if he voluntarily leaves to coach elsewhere within a certain number of years.
As a practical matter, the impact of this approach would be similar to a buyout clause—simply raising the financial bar for deciding to leave. In addition, Michigan should consider having the loan bear interest at the minimum rate set by the IRS, rather than making the loan interest-free. The arrangement could be paired with a separate retention bonus agreement that would pay Howard an additional bonus each year he remains with the school, in an amount sufficient to cover both the interest due on the loan and the tax on the bonus—so that the program would truly be cost-free to Howard for as long as he remains with the University.